Parkinson’s disease, a complex neurological disorder that affects millions worldwide, has long been a subject of scientific curiosity and medical investigation. In this article, altadiscus‘ll delve into the intricacies of this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments. Join us on this journey to uncover the underlying mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease and the impact it has on those who live with it.

Introduction
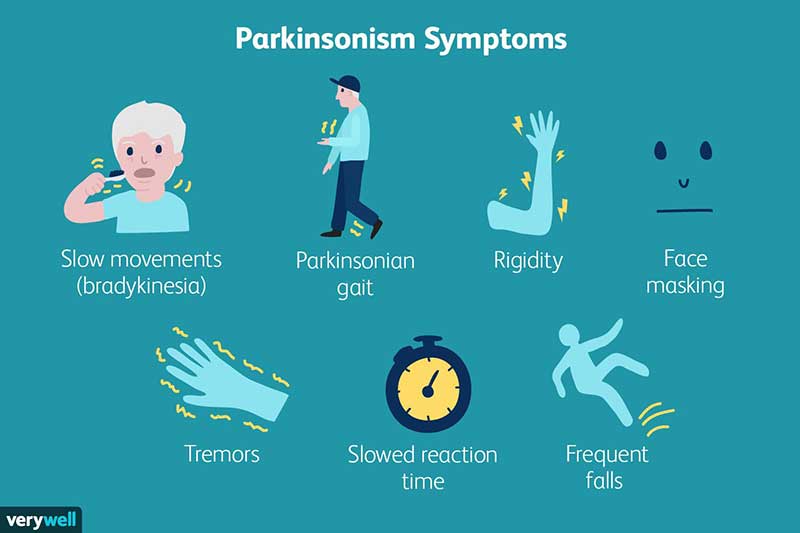
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that predominantly affects the motor system. It is characterized by a variety of symptoms, including tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia (slowed movement), which significantly impact a person’s daily life.What is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease is caused by the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in a region of the brain called the substantia nigra. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating movement and emotions. The loss of dopamine leads to the motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s.The Role of Dopamine: Key Insights into Pathophysiology
Dopamine acts as a messenger between brain cells, allowing smooth and coordinated movements. In Parkinson’s disease, the decreased dopamine levels disrupt this communication, leading to the characteristic motor impairments.Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease extend beyond motor difficulties. Individuals may experience non-motor symptoms like sleep disturbances, cognitive changes, and mood disorders, often preceding the onset of motor problems.Diagnosing Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosing Parkinson’s can be challenging, as there are no specific tests for the disease. Physicians rely on a detailed medical history, neurological examinations, and response to medication to make an accurate diagnosis.
Differentiating Parkinson’s from Other Movement Disorders
Several other movement disorders share similar symptoms with Parkinson’s, making differential diagnosis crucial for effective treatment. Disorders like essential tremor and multiple system atrophy can be mistaken for Parkinson’s.Genetic and Environmental Factors
While most cases of Parkinson’s are sporadic, genetic mutations can increase the risk. Environmental factors like exposure to pesticides and certain toxins have also been linked to the development of the disease.The Stages of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s progression is often categorized into stages, from initial mild motor symptoms to severe impairment. Understanding these stages helps healthcare providers tailor treatments accordingly.Non-Motor Symptoms: Beyond Movement
In addition to motor symptoms, Parkinson’s disease can manifest as sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, and cognitive changes. These non-motor symptoms significantly impact a person’s quality of life.Current Medical Treatments
While there is no cure for Parkinson’s, various medications can help manage its symptoms. Levodopa, a precursor to dopamine, remains a cornerstone treatment, effectively alleviating motor impairments.
Emerging Therapies and Research
Ongoing research explores new avenues for Parkinson’s treatment, including deep brain stimulation, gene therapy, and targeted drug development. These promising therapies offer hope for improved outcomes.Lifestyle Strategies for Improved Quality of Life
Individuals with Parkinson’s can enhance their quality of life by adopting healthy lifestyle practices. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and social engagement can contribute to overall well-being.Caring for Individuals with Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s not only affects the individuals diagnosed but also their caregivers. Providing adequate support, education, and resources is essential for managing the challenges posed by the disease.The Emotional and Social Impact
The emotional toll of Parkinson’s disease can be significant, leading to feelings of isolation and depression. Establishing a strong support network and seeking professional help are crucial for emotional well-being.Looking to the Future: Progress and Hope
As medical understanding of Parkinson’s disease deepens, there is optimism for breakthroughs in treatment and even potential prevention. Ongoing research and collaborative efforts hold the promise of a brighter future for those living with Parkinson’s.Revitalize Your Skin with Collagen Creams
Conclusion
Parkinson’s disease, while complex and challenging, continues to be a focal point of medical research and innovation. By understanding its underlying mechanisms, recognizing its diverse symptoms, and embracing holistic approaches to care, we can make significant strides in improving the lives of individuals with Parkinson’s. With unwavering dedication and ongoing advancements, the path ahead holds the potential for enhanced treatments, increased support, and a world where Parkinson’s is better understood and managed.Can Food Poisoning Cause Parkinson’s Disease?
Food poisoning is typically caused by consuming contaminated food or water. While there are many common causes of food poisoning, such as bacteria like Salmonella or E. coli, there is currently no evidence linking it directly to Parkinson’s disease. However, certain pesticides or chemicals found in some food may increase the risk of developing the condition.


